🌒 Chang’e-6: China’s Bold Mission to the Moon’s Far Side
 |
🚀 Introduction
On May 3, 2024, the world watched as China launched Chang’e-6, a mission that would make history by doing what no space agency had ever done before: return samples from the far side of the Moon. This high-stakes, high-tech operation not only showcased China’s growing space capabilities but also pushed humanity deeper into uncharted lunar territory.
Let’s take a deep dive into this groundbreaking mission — from the hardware to the science, from international collaborations to global impact.
🌕 What Is Chang’e-6?
 |
China's moon mission Chang'e-6: Here's ... |
Chang’e-6 is part of China’s ambitious Chang’e lunar exploration program, named after the Chinese Moon goddess. Following the success of Chang’e-5, which returned near-side Moon samples in 2020, Chang’e-6 took on a more daring challenge: landing and collecting material from the far side of the Moon, which is never visible from Earth.
This is the first-ever sample return mission from the lunar far side — a scientific and engineering feat that no other nation has achieved.
🎯 Mission Objectives
 |
Chang'e-6 delivers first lunar far side ... |
The mission had several key goals:
-
Collect 1.9+ kilograms of lunar rock and soil from the Apollo Basin, a massive crater within the South Pole-Aitken region.
-
Return the samples to Earth for detailed analysis of far-side geology and evolution.
-
Test autonomous ascent and docking technologies, crucial for future lunar base missions.
-
Host international science payloads, including experiments from France, Pakistan, Italy, and Sweden.
🛠️ Tech Behind the Mission
 |
Chang'e 6 Lunar Probe - Civilsdaily |
-
Orbiter: Remained in lunar orbit, awaiting the ascent module.
-
Lander: Touched down on the Moon’s far side and conducted sampling.
-
Ascender: Launched the collected material into lunar orbit.
-
Return Capsule: Carried the samples safely back to Earth.
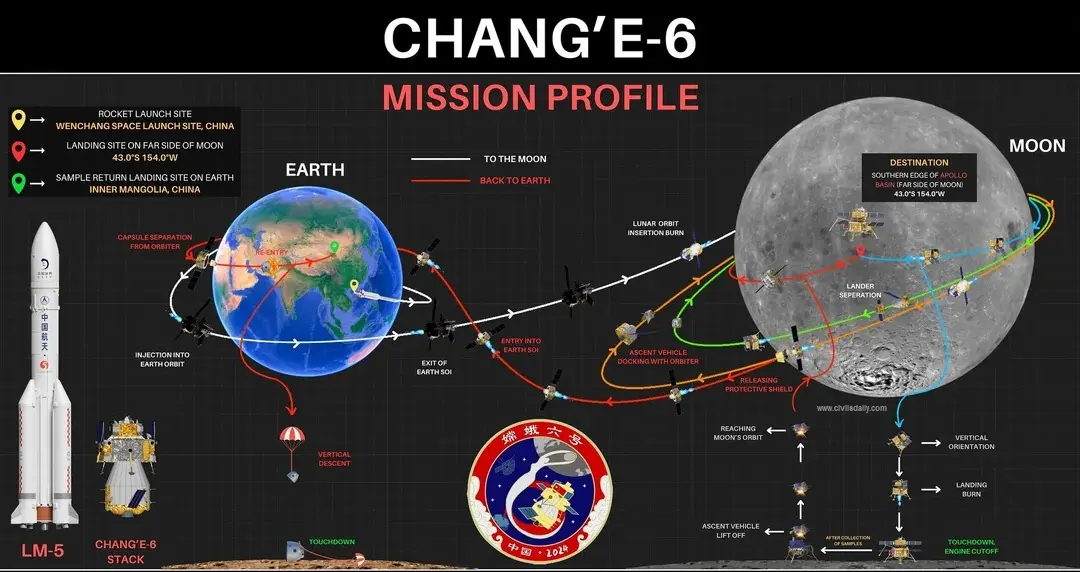
Communications were maintained using Queqiao-2, a relay satellite orbiting beyond the Moon — since direct Earth contact isn’t possible on the far side.
📆 Launch & Timeline
space endeavors ... |
-
Launch Vehicle: Long March 5
-
Launch Date: 3 May 2024, from Wenchang, China
-
Landing on Moon: 1 June 2024 (Apollo Basin)
-
Sample Collection: 1–3 June 2024
-
Return to Earth: 25 June 2024, Inner Mongolia
-
Total Mission Duration: 53 days
-
Sample Collected: 1.935 kg of lunar material
This timeline is a textbook example of precision planning and execution.
🌑 Why the Far Side Matters
The Moon’s far side is a scientific treasure chest. It has:
-
Older crust than the near side, providing insight into the early solar system.
-
A lack of lava flooding, meaning surface features are better preserved.
-
Potential for future radio astronomy bases, away from Earth’s interference.
By analyzing these samples, scientists can unlock clues about the Moon’s formation, early planetary collisions, and even Earth’s own history.
🌍 Global Collaborations
 |
Chang'e 6 Mission Heads to the Moon ... |
Chang’e-6 also carried international science payloads:
-
🇫🇷 France’s DORN instrument measured gas release from the lunar surface.
-
🇵🇰 Pakistan’s ICE Cube-Q CubeSat conducted space environment studies.
-
🇸🇪 Sweden’s NILS instrument studied energetic particles near the Moon.
-
🇮🇹 Italy’s INRRI retroreflector aided in precise laser measurements.
Despite space being a competitive arena, Chang’e-6 highlighted that science can still unite nations, even in geopolitically tense times.
🧠 Challenges of the Far Side
 |
Farside Return on Chang'e ... |
Landing and working on the Moon’s far side is no walk in the lunar park. The mission faced:
-
Communication blackouts, handled via relay satellites.
-
Extreme terrain, requiring precision landing.
-
Autonomous sampling and ascent, with no real-time human control.
-
Thermal extremes and long nights, stretching tech limits.
These hurdles make the mission’s success even more impressive.
🚀 Why Chang’e-6 Is a Big Deal
This mission isn’t just another Moon moment — it’s a game-changer.
-
Technological Milestone: Mastery of far-side operations and sample returns.
-
Scientific Leap: First far-side samples open up entirely new areas of lunar science.
-
Strategic Signal: China is positioning itself as a major player in the new space race, aiming for crewed Moon missions and bases in the 2030s.
It also boosts China’s credibility in both science and diplomacy.
🔭 What’s Next?
Chang’e-6 is part of a bigger vision. China plans to:
-
Launch Chang’e-7 to explore the Moon’s South Pole.
-
Follow with Chang’e-8, which may test 3D printing on the lunar surface.
-
Establish a lunar research station with international partners by the 2030s.
Meanwhile, other countries — including the US, India, Japan, and private companies — are also racing back to the Moon.
The new space race is here, and it’s lunar-powered.
🌟 Conclusion
Chang’e-6 marks a monumental step not just for China, but for humanity. It proves that we can land, sample, and return material from the Moon’s far side — and that international cooperation in space exploration is still very much alive.
As we dream of Moon bases, Mars colonies, and beyond, missions like Chang’e-6 are the milestones lighting the path. 🌕
Slug: change-6-mission
Focus Keyphrase: Chang’e-6 mission
Meta Description: Chang’e-6 has made history by returning the first samples from the Moon’s far side. Learn how this mission redefines space exploration.
Comments
Post a Comment