🔭 James Webb Just Saw the Oldest Galaxy Ever – Here’s What That Means
🌌 Introduction: A Glimpse into the Universe's Baby Album
On a clear cosmic day (a few billion years ago), light left a newly forming galaxy — and after traveling across 13.5 billion light-years, it finally hit the golden mirror of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
The result?
We’ve officially spotted the oldest galaxy ever observed.
But this isn’t just about distance. It’s about time, cosmic origin, and rewriting what we thought we knew about the birth of galaxies.
🧬 What Did James Webb Discover?
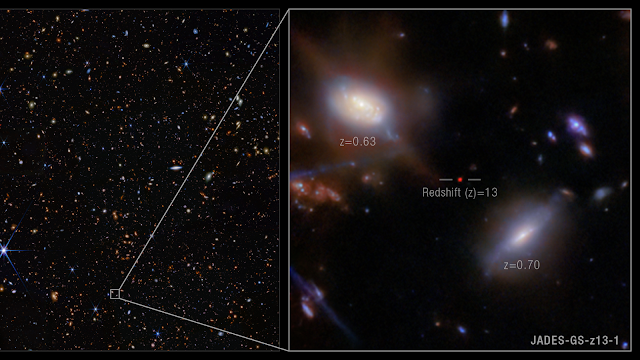
In late 2023, JWST detected a galaxy named JADES-GS-z13-0 (yes, a bit of a mouthful), located at a redshift of z ~ 13.2, which places it roughly 325 million years after the Big Bang.
That might sound like a lot — but in cosmic terms, it’s practically the “hello world” moment of the universe.
This galaxy is now the oldest and most distant known in existence.
🔭 Why This Galaxy Matters
-
Age & Time Travel
Light from this galaxy started traveling to us over 13.5 billion years ago. Observing it is like looking into the early chapters of the universe's storybook. -
Surprising Size & Structure
Scientists expected early galaxies to be small and chaotic.
But JADES-GS-z13-0 is surprisingly mature — suggesting galaxies formed much faster than previously thought. -
Redshift Revelation
Webb’s spectrographs confirmed the galaxy’s age via its redshift — how much its light has been stretched due to the universe expanding.
🔍 What Is Redshift, Anyway?
Redshift is the cosmic version of a Doppler effect.
As objects move away from us, their light stretches into the red spectrum. The higher the redshift, the farther (and older) the object.
JWST is designed to detect infrared light, making it perfect for spotting high-redshift (aka ancient) galaxies that Hubble simply couldn’t see.
🧠 What Does This Mean for Science?
1. Rethinking Galaxy Formation Timelines
If galaxies like JADES-GS-z13-0 existed this early, maybe galaxy formation began far sooner than our models predicted.
2. Hints of Hidden Physics?
Some scientists are even asking: Could this force us to revise our models of the Big Bang or early cosmic inflation?
3. Fuel for Future Missions
This is only the beginning — Webb has many years left, and each new discovery opens a dozen new questions.
🧪 How Webb Found It
This discovery came from the JADES (JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey) program — an ultra-deep look at distant galaxies.
Tools used:
-
NIRCam (Near Infrared Camera)
-
NIRSpec (Near Infrared Spectrograph)
Together, these instruments gathered light from the oldest corners of space and helped confirm the galaxy’s identity.
🔮 What’s Next?
-
Even older galaxies may still be waiting — JWST could find galaxies at z ~ 15 or more.
-
Astronomers are scanning light signatures for first-generation stars (Population III).
-
We may discover early black holes, primitive star clusters, and even early cosmic collisions.
💫 Why It Matters Beyond Science
-
Educational goldmine: Students today are learning from discoveries made just weeks ago.
-
Human inspiration: Seeing the first galaxies ever formed connects us to a grander timeline.
-
Technological flex: JWST proves how far our telescopes (and imagination) have come since Hubble’s launch in 1990.
🧠 Fun Fact Section
Q: How far is 13.5 billion light-years in kilometers?
A: Around 127,620,000,000,000,000,000,000 km (yup, that’s 127 sextillion 😲)
Q: Can we ever reach this galaxy?
A: Not with current tech — but we can keep watching and learning!
Q: What if even older galaxies exist?
A: That’s the dream — Webb is just getting started.
🧠 BONUS: What Makes James Webb So Special?
🔧 1. It Sees What Hubble Can’t
While Hubble looks mainly in visible and ultraviolet light, James Webb specializes in infrared — the kind of light stretched by billions of years of cosmic expansion. This allows JWST to:
-
Detect older, colder, and dust-shrouded objects
-
See through gas clouds where stars are born
-
Catch galaxies that even Hubble missed
❄️ 2. A Telescope That Lives in Shadow
To see such faint infrared light, Webb has to be ultra-cold. It orbits far beyond the Moon at Lagrange Point 2 (L2), always shielded from sunlight by a giant tennis-court-sized sunshield. Its instruments operate at -233°C!
This extreme engineering is why it took over $10 billion and nearly 30 years to launch.
🌌 3. Population III Stars – The First Sparks
Scientists hope JWST will soon spot signs of Population III stars — the first stars ever formed, made purely of hydrogen and helium. We’ve never seen them, but they’re believed to be:
-
Massive and short-lived
-
Responsible for seeding heavier elements like carbon and oxygen
-
The ultimate key to understanding how everything began
If JWST spots even one… it would rewrite cosmic history.
With all this power, James Webb isn’t just a telescope — it’s a time machine built by humanity to touch the edge of forever. 🌠
🌟 Conclusion: We’re Not Just Looking Up — We’re Looking Back in Time
James Webb has handed us a window to the universe’s first breath.
With each pixel of ancient light, we peel back another layer of the cosmos and inch closer to answering humanity’s biggest question:
Where did we come from?
And the best part?
This is just the beginning. 🌌
Slug: james-webb-oldest-galaxy
Focus Keyphrase: oldest galaxy James Webb
Meta Description: James Webb has spotted the most ancient galaxy ever observed. Discover how this discovery reshapes our understanding of the universe’s origin and what lies ahead for astronomy.


Comments
Post a Comment